- Today
- Total
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- sort
- swift 알고리즘
- rxswift
- programmers
- 정렬
- 프로그래머스
- datastructure
- 알고리즘
- 다트
- 프로그래머스 swift
- programmer
- Design Pattern
- coding test
- 프로그래머스 level1
- swift
- 코테
- dart
- 스위프트
- 디자인패턴
- 자료구조
- 정렬알고리즘
- 코딩테스트
- 프로그래머스 레벨2
- swift 코딩테스트
- Algorithm
- swift split
- 스위프트디자인패턴
- 정렬 알고리즘
- 감성에세이
- 디자인 패턴
Bill Kim's Life...
[자료구조] Graph(그래프) : 비선형(Non-Linear) 자료구조, 최단거리/최소거리 알고리즘 본문
[자료구조] Graph(그래프) : 비선형(Non-Linear) 자료구조, 최단거리/최소거리 알고리즘
billnjoyce 2020. 6. 12. 13:53자료구조의 한 종류인 Graph(그래프)에 대해서 살펴봅니다.
#. 구독 대상
- 컴퓨터 및 소프트웨어 공학과 관련자
- 자료구조 개념을 잡고 싶으신 분
- 소프트웨어 관련 종사자
- 기타 컴퓨터 공학에 관심이 있으신 분
- 기타 소프트웨어 개발과 지식에 관심이 있으신 모든 분들
- Swift 언어를 활용하여 자료구조를 공부해보고 싶으신 분들
Graph(그래프)
그래프(Graph)는 비선형(Non-Linear) 자료구조로서 노드(Node)와 간선(Edge)로 구성된 형태를 가진 네트워크 모델의 자료구조입니다.
객체(Node) 간의 관계를 선(Edge)으로 연결하여 표현하는 형태로서 각 정점 간에는 부모-자식 관계가 없습니다.
간선에 방향과 가중치를 두어서 다양한 분야에서 활용가능한 자료구조 중 하나입니다.
최단 경로 찾기 및 저렴한 항공편 검색 등 다양한 분야에서 그래프를 활용할 수 있습니다.
본 강의에서는 간략한 그래프의 용어와 개념에 대해서 설명을 합니다. 좀 더 깊은 개념 및 그래프 탐색 등의 내용은 다른 강의에서 별도로 설명할 예정입니다.
기본 용어
그래프(Graph)에서 사용하는 기본적인 용어들은 아래와 같습니다.
1. Vertex(Node, 정점) : 정점으로서 데이터가 저장되는 기본 객체
2. Edge(간선) : 간선으로서 정점을 연결하는 선
3. Adjacent(인접) : 한 정점에서 간선을 한번에 갈 수 있으면 해당 정점들은 인접하다고 할 수 있습니다.
4. Degree(차수) : 한 정점이 가지고 있는 간선(Edge)의 수
5. 진입 차수(In-degree) : 방향 그래프에서 외부에서 오는 간선의 수
6. 진출 차수(Out-degree) : 방향 그래프에서 외부로 향하는 간선의 수
7. 경로 길이(Path Length) : 경로를 구성하는데 사용된 간선의 수
8. 단순 경로(Simple Path) : 경로 중에서 반복되는 정점이 없는 경우
9. 사이클(Cycle) : 단순 경로의 시작 정점과 종료 정점이 동일한 경우
위에서 설명한 용어들을 예제로 살펴보면 아래와 같습니다.
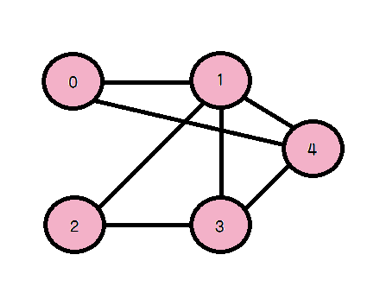
V(Vertex) = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 }
E(Edges) = { 01, 12, 23, 34, 04, 14, 13 }
1 노드의 Degree = 4
3 노드의 인접 노드(Adjacent) = 1, 2, 4
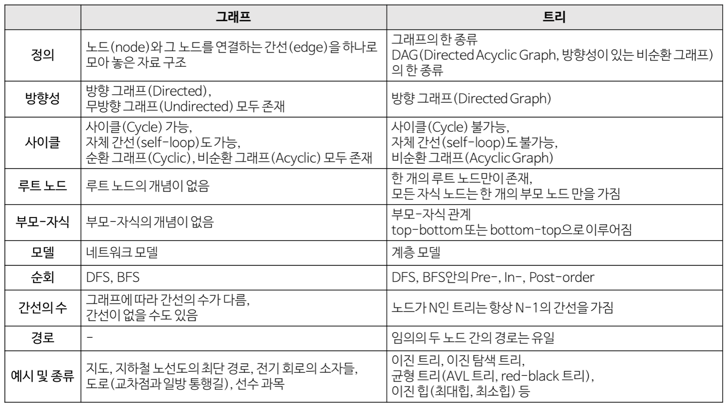
Graph vs Tree
그래프(Graph)와 트리(Tree) 의 차이점을 살펴보면 아래와 같습니다.
Graph 종류
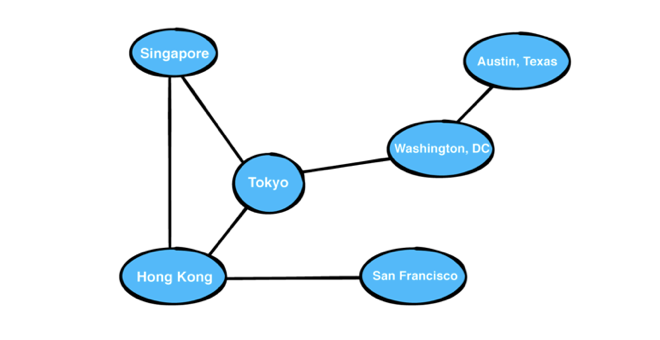
1. 무방향 그래프 : 모든 간선이 양방향인 그래프, 가중치는 양방향 모두 적용
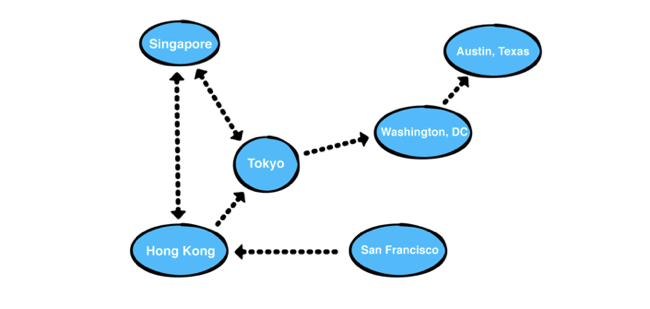
2. 방향 그래프 : 간선들이 방향을 가진 그래프, 방향은 단방향, 양방향이 가능하며 탐색 시 정해진 방향으로만 탐색
3. 연결 그래프 : 무방향 그래프에서 모든 정점 쌍에 대해서 경로가 존재하는 그래프
4. 비연결 그래프 : 무방향 그래프에서 특정 정점 쌍에 사이에 경로가 존재하지 않는 그래프
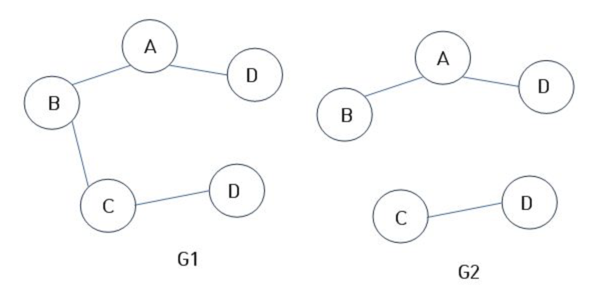
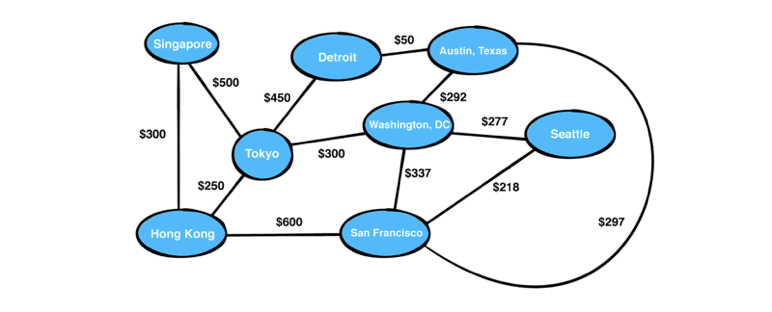
5. 가중치 그래프 : 간선들이 각각 가중치를 가진 그래프, 가중치는 다양한 기준을 활용하여 설정이 가능하며 가중치에 따라서 원하는 경로로 순회가 가능합니다.
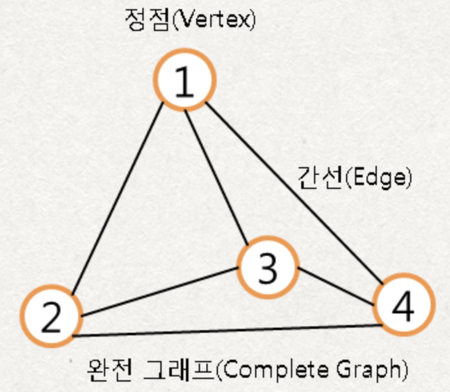
6. 완전 그래프 : 모든 정점들이 인접한 상태인 그래프, n개의 정점이 있다면 모든 정점이 n-1개의 간선을 가지는 그래프
그래프 표현(구현) 방법
Graph를 코드로 구현(표현)하는 방법으로는 크게 두가지 방식이 있습니다.
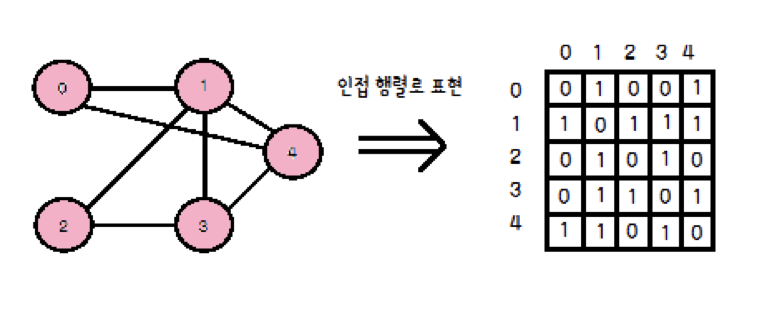
- 인접 행렬(AdjacencyMatrix) :
2차원 배열로 정점과 간선을 표현하는 방식
- 인접 리스트(AdjacencyList) :
각 정점(Vertex)의 리스트는 헤더 노드를 가지고 헤더 노드에 계속 정점을 연결하는 방식
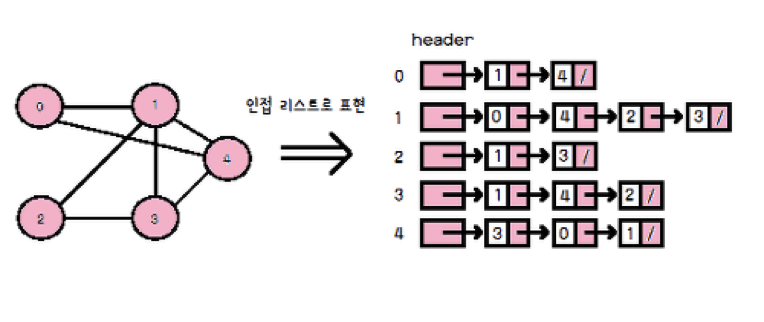
Implementation
Swift를 활용하여 가장 기본적인 Graph를 구현해보겠습니다.
우선 필요한 객체와 메소드는 아래와 같습니다.
필요한 객체
- 정점(Vertex) 객체
- 간선(Edge) 객체
- 그래프(Graph) 추상 객체
- 인접 행렬 및 인접 리스트 객체
- createVertex : 정점을 추가하는 함수
- addDirectedEdge : 방향을 가진 간선을 추가하는 함수
- addUndirectedEdge : 방향이 없는 간선을 추가하는 함수
- weightFrom : 간선 사이에 가중치를 추가하는 함수
- edgeFrom : 간선 리스트를 가져오는 함수
Vertex 클래스
public struct Vertex<T>: Equatable where T: Hashable {
public var data: T
public let index: Int
}
extension Vertex: CustomStringConvertible {
public var description: String {
return "\(index): \(data)"
}
}
extension Vertex: Hashable {
public func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(data)
hasher.combine(index)
}
}
public func ==<T>(lhs: Vertex<T>, rhs: Vertex<T>) -> Bool {
guard lhs.index == rhs.index else {
return false
}
guard lhs.data == rhs.data else {
return false
}
return true
}
Edge 클래스
public struct Edge<T>: Equatable where T: Hashable {
public let from: Vertex<T>
public let to: Vertex<T>
public let weight: Double?
}
extension Edge: CustomStringConvertible {
public var description: String {
guard let unwrappedWeight = weight else {
return "\(from.description) -> \(to.description)"
}
return "\(from.description) -(\(unwrappedWeight))-> \(to.description)"
}
}
extension Edge: Hashable {
public func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(from.description)
hasher.combine(to.description)
hasher.combine(weight)
}
}
public func == <T>(lhs: Edge<T>, rhs: Edge<T>) -> Bool {
guard lhs.from == rhs.from else {
return false
}
guard lhs.to == rhs.to else {
return false
}
guard lhs.weight == rhs.weight else {
return false
}
return true
}
AbstractGraph 클래스
open class AbstractGraph<T>: CustomStringConvertible where T: Hashable {
public required init() {}
public required init(fromGraph graph: AbstractGraph<T>) {
for edge in graph.edges {
let from = createVertex(edge.from.data)
let to = createVertex(edge.to.data)
addDirectedEdge(from, to: to, withWeight: edge.weight)
}
}
open func createVertex(_ data: T) -> Vertex<T> {
fatalError("abstract function called")
}
open func addDirectedEdge(_ from: Vertex<T>, to: Vertex<T>, withWeight weight: Double?) {
fatalError("abstract function called")
}
open func addUndirectedEdge(_ vertices: (Vertex<T>, Vertex<T>), withWeight weight: Double?) {
fatalError("abstract function called")
}
open func weightFrom(_ sourceVertex: Vertex<T>,
to destinationVertex: Vertex<T>) -> Double? {
fatalError("abstract function called")
}
open func edgesFrom(_ sourceVertex: Vertex<T>) -> [Edge<T>] {
fatalError("abstract function called")
}
open var description: String {
fatalError("abstract property accessed")
}
open var vertices: [Vertex<T>] {
fatalError("abstract property accessed")
}
open var edges: [Edge<T>] {
fatalError("abstract property accessed")
}
}
AdjacencyMatrixGraph 클래스
open class AdjacencyMatrixGraph<T>: AbstractGraph<T> where T: Hashable {
// If adjacencyMatrix[i][j] is not nil, then there is an edge from
// vertex i to vertex j.
fileprivate var adjacencyMatrix: [[Double?]] = []
fileprivate var _vertices: [Vertex<T>] = []
public required init() {
super.init()
}
public required init(fromGraph graph: AbstractGraph<T>) {
super.init(fromGraph: graph)
}
open override var vertices: [Vertex<T>] {
return _vertices
}
open override var edges: [Edge<T>] {
var edges = [Edge<T>]()
for row in 0 ..< adjacencyMatrix.count {
for column in 0 ..< adjacencyMatrix.count {
if let weight = adjacencyMatrix[row][column] {
edges.append(Edge(from: vertices[row], to: vertices[column], weight: weight))
}
}
}
return edges
}
// Adds a new vertex to the matrix.
// Performance: possibly O(n^2) because of the resizing of the matrix.
open override func createVertex(_ data: T) -> Vertex<T> {
// check if the vertex already exists
let matchingVertices = vertices.filter { vertex in
return vertex.data == data
}
if matchingVertices.count > 0 {
return matchingVertices.last!
}
// if the vertex doesn't exist, create a new one
let vertex = Vertex(data: data, index: adjacencyMatrix.count)
// Expand each existing row to the right one column.
for i in 0 ..< adjacencyMatrix.count {
adjacencyMatrix[i].append(nil)
}
// Add one new row at the bottom.
let newRow = [Double?](repeating: nil, count: adjacencyMatrix.count + 1)
adjacencyMatrix.append(newRow)
_vertices.append(vertex)
return vertex
}
open override func addDirectedEdge(_ from: Vertex<T>, to: Vertex<T>, withWeight weight: Double?) {
adjacencyMatrix[from.index][to.index] = weight
}
open override func addUndirectedEdge(_ vertices: (Vertex<T>, Vertex<T>), withWeight weight: Double?) {
addDirectedEdge(vertices.0, to: vertices.1, withWeight: weight)
addDirectedEdge(vertices.1, to: vertices.0, withWeight: weight)
}
open override func weightFrom(_ sourceVertex: Vertex<T>, to destinationVertex: Vertex<T>) -> Double? {
return adjacencyMatrix[sourceVertex.index][destinationVertex.index]
}
open override func edgesFrom(_ sourceVertex: Vertex<T>) -> [Edge<T>] {
var outEdges = [Edge<T>]()
let fromIndex = sourceVertex.index
for column in 0..<adjacencyMatrix.count {
if let weight = adjacencyMatrix[fromIndex][column] {
outEdges.append(Edge(from: sourceVertex, to: vertices[column], weight: weight))
}
}
return outEdges
}
open override var description: String {
var grid = [String]()
let n = self.adjacencyMatrix.count
for i in 0..<n {
var row = ""
for j in 0..<n {
if let value = self.adjacencyMatrix[i][j] {
let number = NSString(format: "%.1f", value)
row += "\(value >= 0 ? " " : "")\(number) "
} else {
row += " ø "
}
}
grid.append(row)
}
return (grid as NSArray).componentsJoined(by: "\n")
}
}
AdjacencyListGraph 클래스
private class EdgeList<T> where T: Hashable {
var vertex: Vertex<T>
var edges: [Edge<T>]?
init(vertex: Vertex<T>) {
self.vertex = vertex
}
func addEdge(_ edge: Edge<T>) {
edges?.append(edge)
}
}
open class AdjacencyListGraph<T>: AbstractGraph<T> where T: Hashable {
fileprivate var adjacencyList: [EdgeList<T>] = []
public required init() {
super.init()
}
public required init(fromGraph graph: AbstractGraph<T>) {
super.init(fromGraph: graph)
}
open override var vertices: [Vertex<T>] {
var vertices = [Vertex<T>]()
for edgeList in adjacencyList {
vertices.append(edgeList.vertex)
}
return vertices
}
open override var edges: [Edge<T>] {
var allEdges = Set<Edge<T>>()
for edgeList in adjacencyList {
guard let edges = edgeList.edges else {
continue
}
for edge in edges {
allEdges.insert(edge)
}
}
return Array(allEdges)
}
open override func createVertex(_ data: T) -> Vertex<T> {
// check if the vertex already exists
let matchingVertices = vertices.filter { vertex in
return vertex.data == data
}
if matchingVertices.count > 0 {
return matchingVertices.last!
}
// if the vertex doesn't exist, create a new one
let vertex = Vertex(data: data, index: adjacencyList.count)
adjacencyList.append(EdgeList(vertex: vertex))
return vertex
}
open override func addDirectedEdge(_ from: Vertex<T>, to: Vertex<T>, withWeight weight: Double?) {
let edge = Edge(from: from, to: to, weight: weight)
let edgeList = adjacencyList[from.index]
if edgeList.edges != nil {
edgeList.addEdge(edge)
} else {
edgeList.edges = [edge]
}
}
open override func addUndirectedEdge(_ vertices: (Vertex<T>, Vertex<T>), withWeight weight: Double?) {
addDirectedEdge(vertices.0, to: vertices.1, withWeight: weight)
addDirectedEdge(vertices.1, to: vertices.0, withWeight: weight)
}
open override func weightFrom(_ sourceVertex: Vertex<T>, to destinationVertex: Vertex<T>) -> Double? {
guard let edges = adjacencyList[sourceVertex.index].edges else {
return nil
}
for edge: Edge<T> in edges {
if edge.to == destinationVertex {
return edge.weight
}
}
return nil
}
open override func edgesFrom(_ sourceVertex: Vertex<T>) -> [Edge<T>] {
return adjacencyList[sourceVertex.index].edges ?? []
}
open override var description: String {
var rows = [String]()
for edgeList in adjacencyList {
guard let edges = edgeList.edges else {
continue
}
var row = [String]()
for edge in edges {
var value = "\(edge.to.data)"
if edge.weight != nil {
value = "(\(value): \(edge.weight!))"
}
row.append(value)
}
rows.append("\(edgeList.vertex.data) -> [\(row.joined(separator: ", "))]")
}
return rows.joined(separator: "\n")
}
}
사용 예시
// 인접 리스트 방식 사용 예제
let graphList = AdjacencyListGraph<Int>()
var v1 = graphList.createVertex(1)
var v2 = graphList.createVertex(2)
var v3 = graphList.createVertex(3)
var v4 = graphList.createVertex(4)
var v5 = graphList.createVertex(5)
graphList.addDirectedEdge(v1, to: v2, withWeight: 1.0)
graphList.addDirectedEdge(v2, to: v3, withWeight: 1.0)
graphList.addDirectedEdge(v3, to: v4, withWeight: 4.5)
graphList.addDirectedEdge(v4, to: v1, withWeight: 2.8)
graphList.addDirectedEdge(v2, to: v5, withWeight: 3.2)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v1 to v2 (1.0)
graphList.weightFrom(v1, to: v2)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v1 to v3 (nil, since there is not an edge)
graphList.weightFrom(v1, to: v3)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v3 to v4 (4.5)
graphList.weightFrom(v3, to: v4)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v4 to v1 (2.8)
graphList.weightFrom(v4, to: v1)
print(graphList)
// 1 -> [(2: 1.0)]
// 2 -> [(3: 1.0), (5: 3.2)]
// 3 -> [(4: 4.5)]
// 4 -> [(1: 2.8)]
print(graphList.edgesFrom(v2))
// [1: 2 -(1.0)-> 2: 3, 1: 2 -(3.2)-> 4: 5]
// 인접 행렬 방식 사용 예제
let graphMatrix = AdjacencyMatrixGraph<Int>()
v1 = graphMatrix.createVertex(1)
v2 = graphMatrix.createVertex(2)
v3 = graphMatrix.createVertex(3)
v4 = graphMatrix.createVertex(4)
v5 = graphMatrix.createVertex(5)
graphMatrix.addDirectedEdge(v1, to: v2, withWeight: 1.0)
graphMatrix.addDirectedEdge(v2, to: v3, withWeight: 1.0)
graphMatrix.addDirectedEdge(v3, to: v4, withWeight: 4.5)
graphMatrix.addDirectedEdge(v4, to: v1, withWeight: 2.8)
graphMatrix.addDirectedEdge(v2, to: v5, withWeight: 3.2)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v1 to v2 (1.0)
graphMatrix.weightFrom(v1, to: v2)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v1 to v3 (nil, since there is not an edge)
graphMatrix.weightFrom(v1, to: v3)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v3 to v4 (4.5)
graphMatrix.weightFrom(v3, to: v4)
// Returns the weight of the edge from v4 to v1 (2.8)
graphMatrix.weightFrom(v4, to: v1)
print(graphMatrix)
// ø 1.0 ø ø ø
// ø ø 1.0 ø 3.2
// ø ø ø 4.5 ø
// 2.8 ø ø ø ø
// ø ø ø ø ø
print(graphMatrix.edgesFrom(v2))
// [1: 2 -(1.0)-> 2: 3, 1: 2 -(3.2)-> 4: 5]
이상으로 자료구조의 Graph(그래프)에 대해서 살펴보았습니다.
그럼 즐겁고 행복한 금요일 되세요. ^^
감사합니다.
www.slideshare.net/BillKim8/swift-data-structure-graph-234745668
[Swift] Data Structure - Graph
Swift를 활용하여 자료구조에 대해서 설명하는 강의 자료입니다. 본 강의는 Graph(그래프) 에 대해서 구체적으로 예제와 함께 설명을 하는 강의 자료입니다.
www.slideshare.net
[참고 자료(References)]
[1] Graph : https://ehdrjsdlzzzz.github.io/2019/01/21/Graph/
[2] [Swift Algorithm Club 번역] 그래프 (Graph) : https://oaksong.github.io/2018/04/08/swift-algorithm-club-ko-graph/
[3] Swift로 그래프 탐색 알고리즘을 실전 문제에 적용해보기 - BFS 편 : https://wlaxhrl.tistory.com/89
[4] Graph 자료구조 : https://yagom.net/forums/topic/graph-자료구조-2/
[5] [Data Structure] 그래프 순회, 탐색(DFS) - 자료 구조 : https://palpit.tistory.com/898
[6] DFS (Depth-First Search) BFS (Breadth-First Search) 개념 : https://hucet.tistory.com/83
[7] 자료구조 그래프(Graph) : https://yeolco.tistory.com/66
[8] 자료구조 :: 그래프(1) "정의, 그래프의 구현" : http://egloos.zum.com/printf/v/755618
[9] [알고리즘] BFS & DFS : https://hyesunzzang.tistory.com/186
[10] 자료구조 #4 그래프(Graph) : https://nextcube.tistory.com/190?category=459354
'CS(컴퓨터 과학) > Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] BFS(너비 우선 탐색) : 그래프, 최단/최소 경로를 구해보자 (0) | 2020.06.12 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] DFS(깊이 우선 탐색) : 그래프, 모든 경로를 구해보자 (0) | 2020.06.12 |
| [자료구조] Binary Tree(이진 트리) : 자식이 2개인 트리, 검색이 빠름 (0) | 2020.06.12 |
| [자료구조] Tree(트리) : 계층적 자료구조 (0) | 2020.06.12 |
| [자료구조] Heap(힙) : 이진 트리를 배열로 표시, 최대값/최소값 빨리 찾기 (0) | 2020.06.12 |





